Of course, the right sequence requires the founders or the CEO to start with a Corporate Strategy (nice if it is finalized first) that serves as the foundation for future Marketing and Sales strategies.
Let’s start with an explanation. Sales strategy is a company’s plan to achieve its revenue goals. The sales strategy describes how a business will win, retain, and develop customers.
It is clear that a template that fits everyone doesn’t exist, and I’m going to propose a general outline that may be applicable to most of the technology companies that sell software.
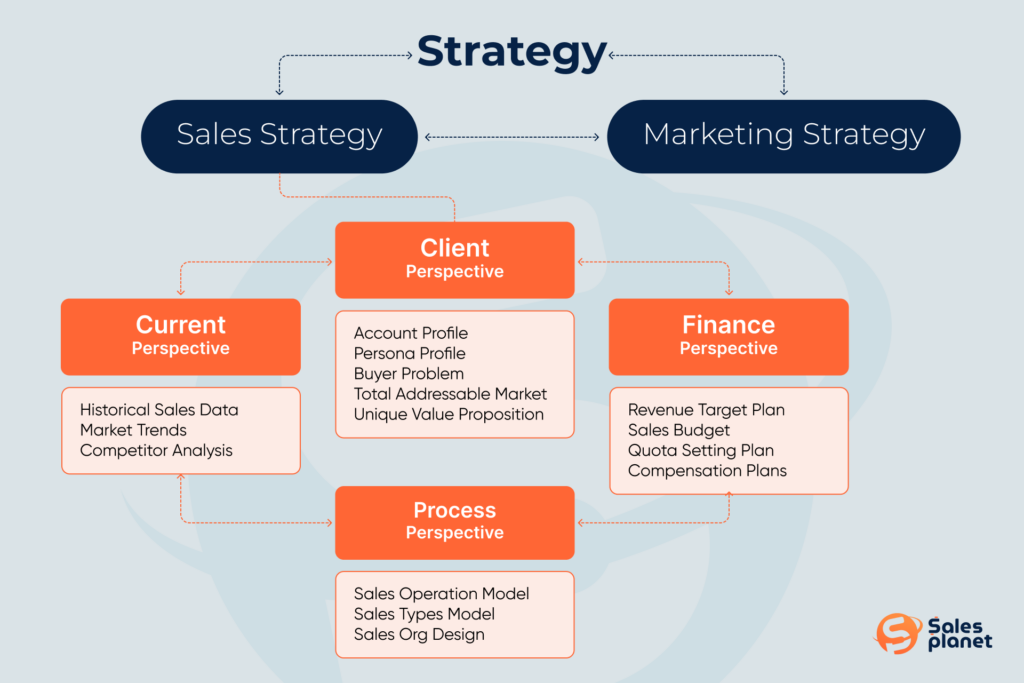
Analysis – history and current positions
Understanding where your company stands is crucial. This includes reviewing historical sales data, analyzing market trends, and assessing your current position relative to competitors. It establishes a baseline for improvement and growth.
Account Profile (Ideal company profiles)
An Account Profile is a detailed description of the types of companies that are the best fit for your services. Identifying these profiles allows your sales team to focus their efforts on high-potential leads and avoid wasting time on unqualified prospects.
By creating detailed account profiles, you empower your sales and marketing teams to focus on the most promising opportunities, develop tailored messaging, and allocate resources more effectively. Furthermore, reviewing these profiles regularly ensures they evolve with market conditions and your company’s growth strategy.
Persona Profile (target buyer personas)
Outline detailed profiles of the individuals within your target accounts who are most likely to make purchasing decisions. Include their roles, goals, pain points, and decision-making processes to align your strategy with their needs.
Sales Operating Model
The Sales Operating Model defines how your sales organization approaches generating revenue and aligns with your business strategy.
Bottoms-Up Model
This approach leverages your company’s expertise and proven successes to guide sales efforts. It starts with what your team knows best—your core competencies, successful use cases, and existing relationships—and builds upward to scale.
Top-Down Model
This approach starts with market trends, broader industry demands, or large-scale opportunities and adapts your services to meet these needs. It is forward-looking and more speculative, requiring a deeper understanding of macroeconomic forces and emerging trends.
Sales Type Model
A company will experience many types of sales, including new logo acquisition (New Business), retention/renewal sales, and account management with cross and upsell opportunities.
Buyer Problem
Buyers are more inclined to see the tangible benefits when the value proposition speaks to their specific issues. Understanding and articulating buyer problems ensures that your sales strategy revolves around solving their pain points rather than pushing products or services. A deep understanding of buyer problems allows you to differentiate yourself from competitors who may not address those issues as effectively.
Our unique value proposition – products and solutions
In crowded markets (like software development), numerous competitors may offer similar products or services. A UVP highlights what sets you apart. UVP is central to sales strategy planning because it defines what makes your product or service distinct, valuable, and relevant to your target audience. It prevents your offering from being perceived as a commodity and makes it more memorable to potential customers.
Total Addressable Market
It is a critical component of strategic planning because it provides a high-level understanding of the potential revenue opportunity available for a product or service in a market. TAM quantifies the full revenue potential, helping businesses understand the size of the market they can target and how much value they can capture. Also, Calculating TAM ensures that ABM efforts (where you target a group of specific accounts) are scalable and aligned with the business’s broader revenue goals, providing a clear path to ROI.
SWAT analysis of the company
By using a SWOT analysis, sales teams can operate proactively rather than reactively, aligning their strengths to market opportunities while minimizing risks and addressing vulnerabilities. A SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is a foundational tool for developing a robust sales strategy
Revenue Target Plan
Sales Success is measured in numbers. Revenue plan is a vital component of any business strategy because it provides clear, measurable objectives that guide decision-making, resource allocation, and performance evaluation. Clear targets enable teams to measure their progress and identify areas needing improvement.
Sales Budget
Financial planning must be aligned with strategic objectives. The sales budget outlines how financial resources will be distributed to achieve sales goals. This includes investments in sales force, tools, marketing campaigns, business trips, compensation plans, and training.
Sales Org Design
Design your sales team structure, detailing roles and responsibilities. Consider the right mix of account executives, SDRs, and support staff for your strategy. You can stick to hunter-farmer, territory based, expertise based organization structure.
Quota Setting Planning
Setting quotas for frontline sales representatives in the annual strategy document is crucial for aligning organizational objectives with sales execution. Quotas connect frontline sales efforts to broader business goals, ensuring that sales reps are driving the outcomes the organization needs. They set clear, measurable targets for sales reps, eliminating ambiguity and providing a concrete standard for success. It bridges the gap between high-level strategy and day-to-day execution.
Compensation Plans
Compensation plans should drive behaviour of your frontline sales organization. By including them in the strategy document, you ensure they are designed to support the specific goals and objectives outlined in the strategy. They reinforce the priorities set in the strategy, such as new logo acquisition or targeting specific customer segments.
Wrap Up:
That’s it, but don’t forget that even the best planning worths nothing without proper execution. An effective sales strategy is a partnership between vision and action. Execution plans, SLAs, and support functions like sales operations and enablement ensure the strategy is not only clear but also achievable, scalable, and measurable.



